Use these settings to set machine locking policy for protected application. This is where you can enable or disable specific locking parameters (locks), set mandatory locks and enable flexible locking and set changeable locks.
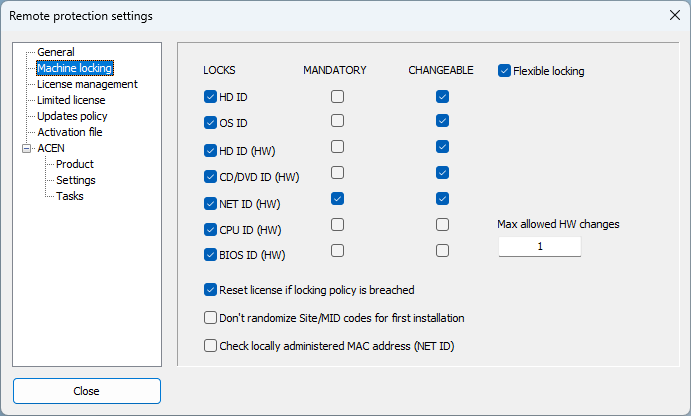
Locking parameters (LOCKS)
There are two software (HD ID, OS ID) and five hardware (HD ID (HW), CD/DVD, NET ID, CPU ID and BIOS ID) locking parameters.
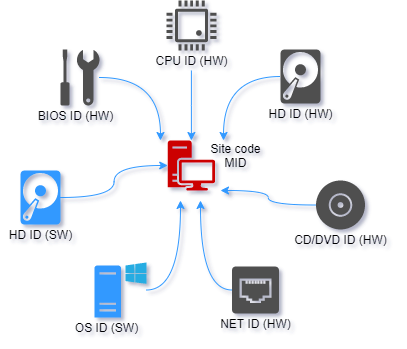
| Lock ID | Description |
|---|---|
| HD ID (SW) | Volume serial number of system hard drive (OS drive). |
| OS ID (SW) | Operating system ID. |
| HD ID (HW) | Hard drive hardware ID. |
| CD ID (HW) | CD/DVD hardware ID. |
| NET ID (HW) | Network adapter hardware ID (MAC address) (see notes below) |
| CPU ID (HW) | Processor ID. |
| BIOS ID (HW) | Motherboard bios manufacturing date/revision. |
Locks from remote machine can be reviewed by decoding MID codes in activation panel.
NET ID notes
- Virtual network adapters are detected and not used for locking.
- Only physical wired or wireless adapters including external USB adapters are used for locking.
- Internal physical Ethernet and SDIO (usually found in tablets) network adapters have priority over external USB network adapters. Only in case no internal network adapters are found protection code will use external USB network adapters for NET ID.
- Use "Check locally administered MAC address (NET ID)" option to handle network adapters locally administered MAC addresses.
- Protection code will scan the list of all available and enabled network adapters starting from the first adapter on the list until it finds the one suitable for locking. Once found, network adapter mac address is detected and used for generation of site/mid codes. Other network adapters are ignored at this point.
- After activation, protection code will scan all network adapters for above mac address on each run. In this way protection code will be able to detect network adapter used for locking even in case adapters list has been changed.
- If adapter is disabled or removed, application will not be able to find adapter with appropriate mac address and will mark this lock as changed. Depending on locking policy this may result in license reset.
Mandatory locks
Each lock can be marked as mandatory.
For example, if NET ID is not marked as mandatory (default) and if Ethernet network adapter is not present on remote machine, protection code will just set NET ID to 0, obtain other locks and generate site/mid codes for remote computer.
If NET ID is marked as mandatory, protected application will require presence of at least single Ethernet network interface (internal or external) on remote computer. In this case locking to MAC address of network interface (NET ID) will be made mandatory for protected application.
This error message will also include error code so that missing mandatory lock can be identified accordingly to the following table:
| Lock ID | Error code |
|---|---|
| HD ID | 1 |
| BIOS ID | 2 |
| OS ID | 3 |
| NET ID | 4 |
| CPU ID | 5 |
| HD HW ID | 6 |
| CD HW ID | 7 |
IMPORTANT: Application will display error message on each run until it is able to obtain mandatory lock. Activation dialog will not be displayed and user will not be able to activate application until protection code is able to obtain mandatory lock.
Flexible machine locking
By default, change in any of selected locking parameters will result in license reset. Application will erase current license, change site/mid codes and request new activation code.
Use flexible machine locking feature to customize default locking policy and to make it more flexible.
Select "Flexible locking" option to enable this feature.
If multiple hardware (HW) locking parameters are marked as changeable, protection code will not reset license as long as total number of changes is lower than defined maximum number of allowed hardware changes.
Maximum number of allowed hardware changes should be lower or same as total number of 'changeable' hardware locking parameters.
Changes tracking is not cumulative. For example, lock can change from original value and then change back to original (no change will be detected) or some different value (change will still be detected as change in single lock). Protection code will count total number of different locks and compare it to selected number of allowed hardware changes.
Don't randomize Site/MID codes for first installation option.
By default, Site/MID codes are always randomized for additional security. In this way, protected application will generate different Site/MID codes even on identical machines or in VM environment.
Select this option if you want to ease default locking policy for your clients. If this option is enabled, Site/MID code will not be additionally randomized on first install. If software locking parameters (HD ID and OS ID) are disabled, protected application will generate same Site/MID codes after HD format or same OS reinstallation. (Default: OFF)
IMPORTANT: If software locking parameters are disabled, end user will be able to reactivate previously removed, transferred or expired license on same computer after hd format or OS reinstall by using original activation code used for first installation!
Check locally administered MAC address (NET ID) option
This option is valid in case NET ID (MAC address locking) is enabled. (Default: OFF)
If selected and in case detected MAC address is locally administered, protection code will try to determine original MAC address of network adapter. In case of failure, such adapter will not be used for locking.
Additionally, if NET ID is marked as mandatory protection code will not use network adapter with locally administered MAC address in case it is not able to determine original MAC address.
Reset license if locking policy is breached option
If enabled and if locking policy is breached, active license will be reset. Machine locking error message box will also be displayed and application will close. If logging is enabled, information about changed locks will also be logged to log file. New Site/MID codes will be generated on next run and application will ask for new activation code. (Default status: ON)
If disabled and if locking policy is breached, protected application will not reset currently active license. No error will be displayed to end user. Instead, activation dialog with different Site/MID codes will be displayed and application will ask for new activation code. If valid activation code is entered application will run as activated. If dialog is closed without valid activation code application will close. Application will ask for new activation code on next run if locking policy is still breached. Locking policy will still be checked on each run and in case it is no longer breached application will start without asking for new activation code.
Notes
- Machine locking is available for REMOTE protection method only.
- Site code / Machine ID (MID) codes from remote computer are based on locking parameters:
- Use Machine ID decoding feature (in activation panel) to get each locking parameter value from remote computer. In this way you can easily compare old and new locking parameters and thus prevent false requests for new activation codes.
- Protection code will scan all cd, dvd, hd devices and network cards on each run. Changing the sequence of cd/dvd/hd drives or primary network adapter will not affect license status. Only in case appropriate device is disabled, removed from system or replaced with another device, protection code will reset license and ask for new activation code.
Changing machine locking policy for new update
If new update is protected with same project settings but with changed machine locking policy (different locks) here is what will happen on remote computers:
1. If previous update is not activated on remote computer new update will generate new (different) pair of Site/MID codes.
2. If previous update is activated on remote computer and some locking parameters are only turned OFF in new update, new update will not reset license (Site/MID code will not change).
3. If previous update is activated on remote computer and some locking parameters are turned ON in new update, new update will display error message, reset license and ask for new activation code.